What is a hot wallet? Compare a hot wallet to a cold wallet in Crypto
A hot wallet is an online cryptocurrency wallet used to manage, store, send, and receive crypto assets that are connected to the internet.
Hello everyone,
One of the first questions that new crypto users often wonder is where to store their digital assets. This issue can be challenging and confusing due to the diversity of options available in the market. Moreover, not implementing appropriate security measures can lead to the loss of funds with no chance of recovery.
There are two fundamental storage methods that users can use: hot wallets and cold wallets. Depending on your circumstances and different times, one type of wallet may be more suitable for you than the other. So what is a hot wallet? How does it work? What are the differences between a hot wallet and a cold wallet? Let's explore together through this article!
It's me again, Neo — Admin — Community Manager of Optimus Finance and Growth Marketing of LECLE Vietnam.
1. What is a hot wallet?
A hot wallet is an online cryptocurrency wallet used to manage, store, send, and receive crypto assets that are connected to the internet. Hot wallets are commonly used for the purpose of trading and making cryptocurrency payments.
Hot wallets are favored for their convenience, allowing users to access their assets quickly and easily. However, due to their internet connectivity, they are more susceptible to attacks and theft.
2. Types of hot wallets
Depending on the classification method, hot wallets can be divided into different types:
Based on the type of device used: web wallets, mobile wallets, and desktop wallets.
Based on control over the private key: custodial wallets and non-custodial wallets.
2.1. Based on the type of device used
Based on the type of device used, management, and accessibility, hot wallets are divided into three types:
Web Wallet: A wallet that is accessed and managed through a web browser. User data and login information are encrypted and stored on the provider's server.
Desktop Wallet: A wallet that is installed and stored on the user's computer using desktop software. Data is encrypted and stored on the computer's hard drive. To secure the wallet, users need to implement protective measures such as strong passwords and antivirus software. This was the first type of hot wallet developed before the emergence of web and mobile wallets.
Mobile Wallet: A wallet that is installed and stored on a smartphone or mobile device (such as a tablet). This type of wallet is often used as mobile applications. Data and private keys are stored on the device, and users can use a PIN or fingerprint to authenticate access.
Currently, web and mobile wallets are much more popular than desktop wallets due to their convenience and easy access.
2.2. According to the control rights
Based on the user's access and control over the private key of the wallet address, hot wallets are divided into two types:
Custodial Wallet: The private key of the wallet is managed by a third-party service provider. They have full control over the user's assets, are responsible for managing the wallet's private key, and sign transactions when the wallet owner performs transactions. Typical examples of custodial wallets are exchange wallets (e.g., Binance, Bybit, Crypto.com).
Non-custodial Wallet: The private key of the wallet is managed by the wallet creator. Users have complete control over their assets, manage the private key themselves, and sign transactions. No one (including the wallet provider) can access the wallet except the wallet owner. Some examples of non-custodial wallets include Coin98 Super App, Metamask, and Trust Wallet.
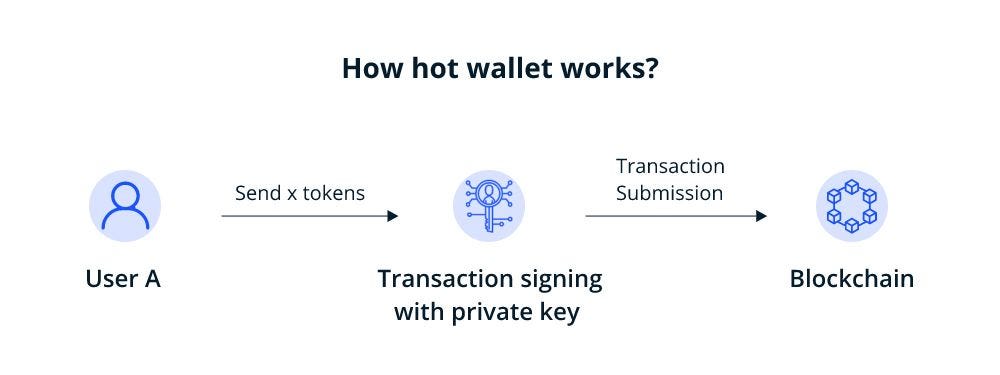
3. How hot wallets work
Firstly, it's important to understand how cryptocurrency wallets operate.
Cryptocurrency wallets work based on two types of keys: Public Key & Private Key, where:
Public Key acts as a wallet address, allowing users to receive crypto assets into the wallet. The Public Key can be freely shared publicly.
Private Key acts as the key to unlocking the wallet, granting users access to the wallet to execute transactions of sending/withdrawing assets from within. Private Key is kept secret and should not be shared with anyone.
When sending cryptocurrency:
The sender uses their private key to access the wallet and sign the transaction within the wallet.
Nodes (computers on the network) will validate and send the transaction to the blockchain.
The transaction is recorded on the blockchain, and the cryptocurrency will be sent to the recipient's wallet.
In essence, hot wallets follow a similar operational process to traditional cryptocurrency wallets, but there are differences depending on the types of wallets.
For Custodial wallets: The transaction signing step is performed by the third-party service provider since they manage the private key. This process involves more parties, which can result in slower transaction speeds.
For Non-custodial wallets: The transaction signing step is performed by the users themselves. Since they have direct control over their private key, the transaction process involves fewer intermediaries, leading to faster transaction speeds.
4. Pros and Cons of hot wallets
4.1. Pros
Hot wallets have the following advantages:
Easy to use: Hot wallets usually have an intuitive interface, easy installation, and user-friendly features.
Convenient: Users can easily perform daily transactions quickly and efficiently.
Online accessibility: With an internet connection, users can access their wallet accounts from anywhere and on any device.
Flexibility: Hot wallets often support multiple cryptocurrencies on different blockchains, allowing users to diversify their investment portfolios.
Low costs: Most hot wallets offer free usage or require minimal transaction fees, saving users money.
Multiple asset management options: For custodial and non-custodial wallets, users can choose to self-manage their assets or entrust control to a third party.
4.2. Cons
However, hot wallets still have some drawbacks, such as:
Low security: Hot wallets are always directly connected to the internet, making them susceptible to viruses or hacking attacks. This compromises the security of the wallet and may put the stored assets at risk.
Dependency on the Internet: To access the wallet and perform transactions, users need an Internet connection. If the network is disrupted or the internet speed is slow, using a hot wallet can become challenging and inconvenient.
5. Comparison between Hot wallets and Cold wallets
In contrast to hot wallets, cold wallets are physical wallets used to store cryptocurrencies without the need for an internet connection. Cold wallets are typically divided into two types:
Hardware wallet: These are hardware devices used to store private keys and public keys. They can be connected to a computer or mobile phone via USB or Bluetooth to facilitate cryptocurrency transactions. Some popular hardware wallets include Trezor and Ledger.
Paper wallet: Public and private keys of the wallet are printed on a piece of paper in the form of QR codes for scanning when performing transactions.
Hot wallets:
Connected to the internet for easy access and quick transactions.
Convenient and user-friendly with intuitive interfaces.
Lower security due to online exposure and potential hacking risks.
Suitable for frequent trading and day-to-day transactions.
Examples include web wallets, desktop wallets, and mobile wallets.
Cold wallets:
Offline storage for enhanced security against cyber threats.
Less convenient compared to hot wallets, as transactions require additional steps like connecting to a device.
High security since private keys are kept offline and away from potential online attacks.
Ideal for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies, providing a safe "cold storage" option.
Examples include hardware wallets and paper wallets.
Both hot and cold wallets serve different purposes and cater to different needs of cryptocurrency users. Hot wallets offer convenience and accessibility for regular transactions, while cold wallets prioritize security for long-term storage and protection of assets. It's essential for users to consider their requirements.
6. How to secure Hot wallets
Because hot wallets are always connected to the internet, their security is more limited compared to cold wallets. However, with proper precautions, hot wallets can still be a useful tool for storing assets securely. Here are some ways to secure hot wallets:
Avoid storing a large amount of assets in the hot wallet and use it primarily for trading and regular transactions.
Diversify and store assets across multiple hot wallets to mitigate the risk of losing all funds in case of an attack.
Always double-check and ensure that you download applications or software updates from the official website of the project.
For non-custodial wallets, store the private key or seed phrase in a secure location and never share these keys with anyone.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) on your hot wallet if available, as an additional layer of security.
Avoid accessing unfamiliar websites or clicking on suspicious links to prevent falling victim to phishing attacks.
Create a separate wallet and store only a small amount of assets for airdrops or interacting with decentralized applications (DApps). Avoid using the same wallet for storing all assets and participating in airdrops.
By following these security measures and staying vigilant, users can enhance the security of their hot wallets and protect their cryptocurrency assets from potential threats. Remember, security should always be a top priority when dealing with digital assets.
7. Frequently asked questions about Hot wallets
7.1. Are hot wallets safe?
The safety of hot wallets depends on various subjective and objective factors.
Subjective factors from users include how they manage their private keys, their connections to unknown platforms, and the security measures they implement.
Objective factors from external sources include risks associated with internet connections, risks related to the storage devices used for the wallet, and the possibility of attacks on the service provider's systems.
While hot wallets can be convenient for daily transactions, users need to understand the potential risks and take necessary precautions to ensure the highest level of security for their assets.
Safety practices such as strong security measures, using trusted platforms, and being aware of potential risks are essential to protect one's assets in hot wallets.
7.2. Can hot wallets be hacked?
Yes, hot wallets can be vulnerable to hacking if they are not properly protected or if necessary security measures are not followed. To minimize the risk of hacking, users should adhere to robust security practices such as those mentioned above. Implementing strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), using trusted platforms, avoiding suspicious links, and keeping private keys secure are essential steps to reduce the chances of a hot wallet being hacked.
However, it's important to note that no security measure can guarantee 100% protection against hacking. Therefore, users should always stay informed about potential threats and take proactive measures to safeguard their cryptocurrency assets. Regularly updating software and following best security practices can significantly enhance the safety of hot wallets.
7.3. When should you use a hot wallet?
Hot wallets are typically used in the following scenarios:
Storing a small amount of cryptocurrency assets: Hot wallets are suitable for holding a limited amount of cryptocurrencies that you intend to use for regular transactions and daily expenses.
Performing quick and convenient daily transactions: Hot wallets are ideal for users who frequently engage in cryptocurrency transactions, such as buying, selling, or making payments.
Utilizing services that accept cryptocurrency payments: Hot wallets can be used for making purchases or payments at merchants and services that accept cryptocurrencies as a form of payment.
Participating in airdrops and interacting with DApps: Hot wallets are useful when engaging with airdrops or using decentralized applications (DApps) on blockchain networks.
8. Closing thoughts
Exactly, the choice of wallet depends on specific use cases and the preferences of the cryptocurrency owner. For newcomers seeking convenience and quick access to their cryptocurrencies or for traders requiring fast transactions, a hot wallet can be a suitable option. Hot wallets are practical for everyday use and frequent transactions, making them convenient for individuals who frequently engage in cryptocurrency activities or make regular crypto payments.
On the other hand, if you are an investor focused on long-term storage and prioritize security above all else, a cold wallet may be a better choice. Cold wallets offer enhanced security by keeping private keys offline and away from potential online threats, making them more suitable for storing larger amounts of cryptocurrencies for the long term.
It is crucial to carefully consider your cryptocurrency goals and requirements when selecting a wallet. Evaluate factors such as convenience, security, and the level of control you desire over your assets. Each type of wallet has its advantages and disadvantages, and understanding your needs will help you make the best choice for managing and securing your cryptocurrency holdings effectively.
What about your thoughts? Don’t hesitate to share with us! 😀
This post is for educational purposes only. All materials I used were the different reference sources. Hope you like and follow us and feel free to reach out to us if there is an exchange of information. Cheers! 🍻
#blockchain #hotwallet #cryptocurrency