What is a smart contract? All the information about Smart Contract
The cryptocurrency industry is rapidly expanding and constantly evolving with innovations in blockchain technology.
Hi everyone,
The cryptocurrency industry is rapidly expanding and constantly evolving with innovations in blockchain technology. One of the factors that sets crypto apart and makes it superior to other fields is the use of smart contracts and their widespread applications.
Dex, NFTs, Marketplaces, and more are all applications created through smart contracts on the blockchain. In today's article, we will explore everything there is to know about Smart Contracts.
And...it's me, again, Neo — Admin — Community Manager of Optimus Finance và Growth Marketing of LECLE Vietnam. Let's go!
1. What is a smart contract?
A 'smart contract' is a term used to refer to a specialized program capable of automatically executing terms and agreements between parties (specifically in this case, computer systems). Smart contracts operate through the advancements in blockchain technology and do not rely on any third-party intermediaries.
Typically, smart contracts operate based on the following four elements:
The contract parties
The terms and conditions
Digital signatures
And the permissioned platform
Each blockchain has its own method for deploying smart contracts, for example, Cosmos has WASM, Polkadot has ink,... However, the most prominent one is still the Smart Contract running on Ethereum's virtual machine (Ethereum Virtual Machine - EVM).
2. Why are smart contracts important?
Smart contracts are an essential element in blockchains and contribute to the efficiency of a particular platform for various reasons.
Essentially, blockchain-based smart contracts enable the creation of trustless protocols. This means that the two parties in the contract can make commitments through the blockchain without needing to know or trust each other. They can ensure that if the conditions of the contract are not met, the contract will not be executed.
Furthermore, the use of smart contracts aims to eliminate the need for intermediaries, significantly reducing operational costs. However, each blockchain has a different method for deploying smart contracts.
In practice, smart contracts enable developers to build a wide range of decentralized applications and tokens. They are utilized in various fields, from new financial tools to infrastructure and gaming experiences. Once added to the blockchain, they are stored like any other cryptocurrency transaction and are typically immutable (though there are some exceptions).
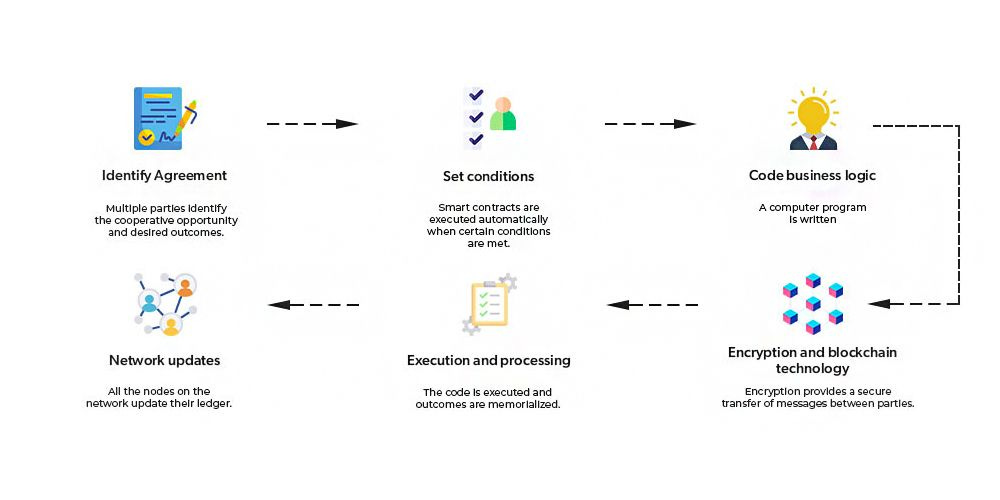
3. How does a smart contract work?
Put simply, a smart contract operates like a deterministic program. This means it executes a specific task when certain predefined conditions are met. Therefore, a smart contract system typically follows 'If... then...' statements.
In the initial phase, the terms of the contract are written in a programming language. They are then encoded, marked with an address, and placed into a block on the blockchain. Once added to a block, this data is distributed and replicated by nodes operating on that blockchain network.
The information stored on the blockchain waits for triggering conditions. When triggered, smart contracts activate and execute certain pre-agreed terms, automatically verifying the fulfillment of commitments outlined in the contract.
On Ethereum, smart contracts are responsible for executing and managing activities that occur on the blockchain when users (addresses) interact with each other. Any address that is not a smart contract is referred to as an Externally Owned Account (EOA). Therefore, smart contracts are controlled by computers, and EOAs are controlled by users.
An Ethereum smart contract consists of a contract code and two public keys:
The first public key is provided by the contract creator.
The other key represents the contract itself, serving as a unique digital identifier for each smart contract.
Smart contracts are deployed through blockchain transactions, and they are only activated when an External Owned Account (EOA) or other smart contracts call them. However, the initial activation always comes from an EOA (user).
For example: If you want to purchase a house from a person named A and make the payment in cryptocurrency through the blockchain. The receipt will then be placed in the smart contract of person A, and they are responsible for delivering the encryption key and the house to you on a specified date as outlined in the contract. If person A does not deliver the key on time, the money will be returned to your account. If it is delivered ahead of schedule, the system will retain both your money and person A's encryption key to be transferred on the correct date.
4. The features of a smart contract
A smart contract is a combination of many outstanding features, bringing improvements over traditional contracts. Specifically, smart contracts possess the following characteristics:
Decentralized: Smart contracts are copied and distributed across all nodes of the Ethereum network. This is a key distinction from other solutions based on centralized servers.
Deterministic: Smart contracts only execute predefined tasks on this platform when all conditions are met. Additionally, the results of a smart contract remain unchanged regardless of the executor.
Automated: Smart contracts can automate various types of tasks, operating as self-executing programs. However, in most cases, if a smart contract is not triggered, it will maintain an 'inactive' state and will not perform any actions.
Immutable: Smart contracts cannot be modified after deployment. They can only be 'deleted' if this functionality was pre-programmed. Therefore, smart contracts can be likened to anti-counterfeiting measures.
Customizable: Before deployment, smart contracts can be encoded in various ways. Hence, they can be used to create various types of decentralized applications (DApps).
Trustless: Two or more parties of a contract can interact through a smart contract without needing to know or trust each other. Furthermore, blockchain technology ensures data accuracy.
Transparency: Since smart contracts are based on a public blockchain, no one can alter their source code, although anyone can view it.
Like conventional contracts, smart contracts are designed to enforce agreement terms, whether it's cryptocurrency exchange, encrypted rights, identity verification, or virtually anything else.
5. Advantages and disadvantages of smart contracts
5.1. Advantages
A programmable code, smart contracts offer high customizability and can be designed in various ways to provide a wide range of services and solutions. Because they are executed automatically through programming on the system, ensuring flexibility in execution.
Smart contracts help save costs in operation. Specifically, deploying smart contracts does not require third-party supervision, printing, shipping, or storage. Furthermore, with decentralized and self-executing programs, smart contracts contribute to cost reduction in operations, leading to increased efficiency.
Smart contracts also ensure transparency and clarity in platform activities. All transactions are conducted on the system and recorded on the blockchain, allowing entities to easily verify the origin of transactions.
Especially in a smart contract, users can only access and view information but cannot edit or remove anything. This ensures the security of important data without interference from relevant parties.
In practice, smart contracts are executed quickly, saving time. Additionally, this type of contract is not limited in terms of usage frequency, allowing continuous applications while maintaining utility throughout operations.
Furthermore, smart contracts have high applicability in various fields. They can create tokenized assets from voting systems, cryptocurrency wallets, decentralized exchanges, and even mobile apps. Additionally, smart contracts can be integrated into aspects such as healthcare, charity, supply chains, management, and decentralized finance (DeFi)...
5.2. Disadvantages
Smart contracts, being based on blockchain systems, are immutable and tamper-proof. Once a smart contract is written, the only way to make changes is by creating a new contract. The unchangeable nature is a significant advantage, although it can be a disadvantage in some cases.
For example, when a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) named 'The DAO' was hacked in 2016, millions of ETH were stolen due to a flaw in their smart contract code. Because their smart contract was immutable, developers couldn't fix the code. This ultimately led to a hard fork, creating Ethereum Classic and Ethereum.
Furthermore, smart contracts are products of the blockchain, which is not yet legally protected. Therefore, if a smart contract has a bug, users may not have government protection of their rights.
Additionally, some argue that centralized systems can provide most of the solutions and functionalities that smart contracts offer. However, the difference lies in the fact that smart contracts run on a decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) network rather than on a centralized server.
6. The applications of smart contracts in crypto and various other fields
Thanks to the outstanding features of smart contracts compared to traditional contracts, they have been widely applied in various fields, delivering significant efficiency gains. Beyond their use in crypto, smart contracts have also been integrated into many different platforms, such as data management, supply chain management, healthcare, insurance, government administration, asset ownership, escrow services, and automotive.
6.1. In the cryptocurrency industry
Fundamentally, most applications provided by centralized systems can be designed similarly to smart contracts on the blockchain. Smart contracts allow developers to create numerous different use cases. Implementing these enhanced contract types promotes faster, more efficient transactions, saving both time and operational costs.
Specifically, smart contracts integrated into decentralized financial applications (DApps) enable users to trade from anywhere without relying on any third-party intermediaries. Additionally, with their decentralized and permissionless nature, smart contract networks can operate cryptocurrency trading systems flexibly and with superior improvements.
For example, smart contracts are employed in cryptocurrency wallets to store various coins and tokens. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap, 1Inch, and blockchain games like Crypto Kitties and Axie Infinity also utilize smart contracts.
6.2. Some other fields
Data Management: Developers can program smart contracts to streamline the data recording process by automating all of those tasks. Smart contracts enable the consistent and transparent storage of data across departments.
Supply Chain Management: Implementing blockchain technology and smart contracts can help track the location of products and reduce the risk of losing goods due to the transparency of data.
Healthcare: Smart contracts contribute to time and cost savings in the healthcare industry by eliminating paper-based systems and insecure data servers.
Election Results: With smart contracts, activities like election manipulation can be prevented with various superior features. In practice, the voting records protected by a ledger would require decryption and strong access rights to access it.
Escrow Processes: Escrow typically refers to a legal agreement in which a third party represents two parties holding a specific amount of money during the completion of a transaction. However, with smart contracts, this contract form helps prevent fraud and reduces risks for both sides of the transaction. Additionally, businesses also use smart contracts to facilitate the escrow process by making it transparent and automatic.
Automotive Manufacturing Industry: Smart contracts automate payments for activities such as maintenance, toll booth passage, and insurance.
7. Closing thoughts
It can be affirmed that smart contracts represent a technological advancement with a profound impact on the cryptocurrency space and many other sectors within society.
Smart contracts appear to be a solid foundation driving the emergence of even more potential applications in the future, promising to bring about valuable innovations.
What about your thoughts? If you want to know further about it, don’t hesitate to share with us! 😀
This post is for educational purposes only. All materials I used were the different reference sources. Hope you like and follow us and feel free to reach out to us if there is an exchange of information. Cheers! 🍻
#smartcontract #blockchain